

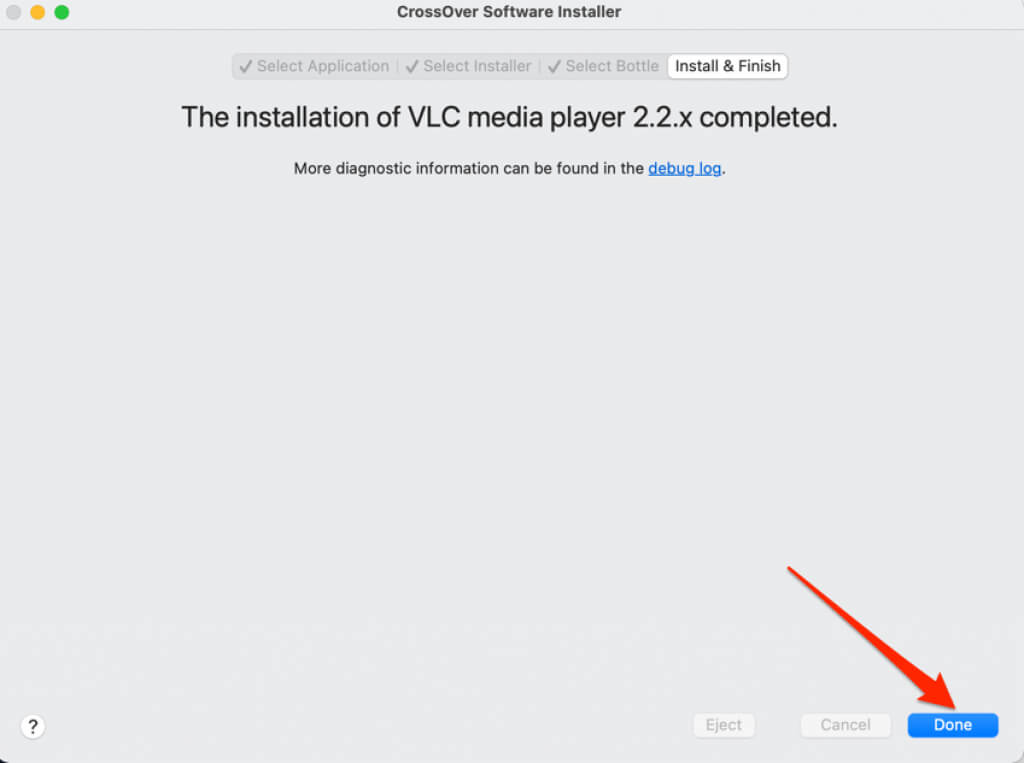
Note down the name of the destination mount point (e.g. Open up a Terminal window and you can mount an ISO image by executing the following command.Method 3: Open and Mount ISO file on Mac Using Terminal Next, select any ISO image you want to mount, and click Open.Once Disk Utility is open, click the File tab on the menu bar and then select Open Disk Image.select Applications in the sidebar, then double-click the Utilities folder and then double-click Disk Utility. Method 2: Open and Mount ISO file on Mac Using Disk Utility When you no longer need to access the mounted drive, just right-click on it and select Eject.You can double-click it to open the drive and view the contents of your ISO image. A new drive will now appear on your desktop.
To start, open a Finder window and navigate to the location of your ISO file, then right-click on it and select “ Open With” -> “ DiskImageMounter (default)“.Method 1: Open and Mount ISO file on Mac with DiskImageMounter A new drive will now appear on your desktop. To start, open a Finder window and navigate to the location of your ISO file, then right-click on it and select Open With -> DiskImageMounter (default). EXE format was, and still is utilized in many operating system, including MS-DOS, Windows, OS/2, OpenVMS and others. There are several versions of this file format, but all serve the same purpose - to start a program.
#OPEN EXE FILE ON MAC FREE HOW TO#
How to open an MSI file on Mac MSI files are not compatible with the Mac operating. The exe file extension is traditionally used for program executable file since the time of first DOS. MSI file, just double-click on it, and the Windows Installer will open it automatically. In this tutorial we’ll show you 3 easy ways to open and mount ISO file on macOS High Sierra. Method 1: Open and Mount ISO file on Mac with DiskImageMounter. How to open an MSI file in Windows 10 MSI files can be opened automatically with the Windows Installer program that is built-in to Windows operating systems. ISO file on your Mac? ISO files are often used to distribute bootable utilities for DOS, Windows, Linux or other operating systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
